- Home
- Exercise Bike Resistance
How Exercise Bike Resistance Works
There are three main types of exercise bike resistance to increase the intensity of the workout. If you understand how the intensity/resistance works in these stationary bikes, you will have a better idea of which type of bike is better suited for use in your home.
Resistance is an important factor in choosing an exercise bike, more so than the actual size of the flywheel. The weight of the flywheel is to provide smoother pedaling; i.e., larger flywheels pedal more smoothly and give you more momentum than smaller ones.
The resistance component is necessary to make pedaling more difficult or easier and to give you a better and more varied workout.
Direct Tension
The first type uses mechanical resistance provided by the friction of moving parts such as a roller or brake pads that apply direct pressure to the flywheel, which is attached to the pedals. Spinner bikes are an example of a bike that uses a brake pad against a weighted flywheel to increase resistance.
Magnetic Brake
A modern design of exercise bike resistance technology is the electromagnetic brake. Used on more expensive uprights and recumbents, it is favored by users because it is extremely quiet, in fact, nearly silent.
The ECB or electromagnetic resistance system feels smoother when pedaling, quickly responds to resistance changes since it is done electronically on the console, and has fewer parts to wear out.
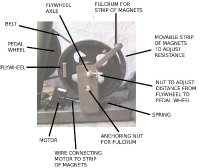
Manual magnetic brake exercise bikes use a tension knob located between the handlebars to work the brake the same way as ECB. The resistance is changed by moving magnets causing eddy currents to create a braking effect to oppose the rotational direction of the flywheel.
As the magnets get closer to the flywheel the drag effect creates the resistance you feel while pedaling. When you dial down the resistance, the magnets are moved away from the flywheel and the bike is easier to pedal.
Air Flow Resistance
Another type of exercise bike resistance comes from pedaling against the airflow of a fan blade located on the front of the bike. The Schwinn AirDyne, a popular bike model that has been in use for decades, is a good example of this design. It uses an open fan instead of a flywheel and creates stronger resistance as pedaling speed increases.
Which to Consider
In both the direct tension and ECB resistance-style of exercise bikes, the level of resistance is selected by the rider who adjusts the amount of pressure applied to the brake. With the tension at the lowest level, the rider can pedal at a fast cadence to expend the highest amount of energy. At the highest resistance level, it becomes difficult to pedal simulating an uphill climb on a road bike.
The open flywheel or air fan bike, however, does not offer adjustable resistance at slow speeds like the other two types of exercise bikes can. The advantage is that it requires more energy to get the larger open flywheel in motion, while a smaller flywheel on a standard stationary bike requires minimal momentum to start out.
Bikes to Suite Every Need
If you understand how exercise bike resistance works, you will have a better idea of which type of bike is better suited for use in your home. Magnetic flywheels are the best overall; they last longer and require less maintenance than mechanical types. The air fan bikes don’t offer adjustable resistance, but have the benefit of cooling air blowing back on you as you pedal harder. Spinner bikes are in a class by themselves and are ideal for anyone wanting intense cycling workouts.
UPDATE: February Exercise Bike Sales are going on now!
Best Bikes For 2026

Best Uprights & Recumbents
Best Indoor Cycling Bikes
Best Minis/Under Desk
Comparison Charts

Upright Bikes
Recumbent Bikes
Buying Guide
Find the right bike at the best price!
Workouts

How to make the time spent exercising fun!
Submit Review

Rave or rant about the exercise bike you purchased online or used at the gym.


